Apart from concerns about incorporating oils in skincare, customers are rapidly becoming more interested in the compounds utilized in their hair care, as well as experts who can assist their scalp health improvement.
Hair products that contain oils when applied to and left on the scalp can have increased efficacy, especially when made with clinically validated active components with small molecular mass and penetration-boosting formulation principles.
Oils in haircare formulations have been used and experimented with for centuries. Different oils are claimed to have different benefits for hair composition, growth, and shine.
Three main types of oils are commonly used in hair care formulations: monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fats.
These oils can be classified according to their positioning on the food pyramid: monounsaturated fats are found at the bottom of the pyramid, polyunsaturated fats are found halfway up the pyramid, and saturated fats are at the top.
Oils in various hair care formulations have shown evidence to help nourish the scalp and hair, protect against environmental damage, add shine and softness, and preserve hair shafts.
Thus, to elaborate on its efficiency, we’ll explore the different roles and responsibilities of oils in haircare formulations, and how to use them to achieve the desired results.
We’ll also examine the different oil types available and their benefits. Finally, we’ll consider some scientific shreds of hair-oil interaction, hair oil blends, the role of essential oils used in haircare formulation, the advantages of using oils, and methods of hair oiling
Incorporating Oils In Haircare
We all know that incorporating oils in several hair products can bring immense benefits to hair and this has been experimented with well enough since ancient times when ancient inventors started experimenting with oils that could be infused in different hair cosmetics.
Many hair cosmetic items discovered seemed to work well because they include formulating various oils in shampoo, heat protectants, hair drops, hair serums, hair oil blends and hair masks.
Apart from that, we need to understand why incorporating oils in hair care formulations was so important in ancient times that stretched its vitality till now, and that is; natural hair oil called sebum is produced by glands around each follicle in humans.
Similar oils, such as lanolin, are produced by other mammals. Artificial hair oils, like natural oils, can reduce scalp dryness by producing hydrophobic films that reduce transepidermal water loss and evaporation of water from the skin.
Hair oils can prevent the absorption of water, which damages hair strands due to continuous hygral stress as the hair swells when wet and contracts as it dries.
A range of commercial and traditional hair oils are made with mineral and vegetable oils before the start of plant-based oils.
But on looking over the topic, in our modern times, people have become severely conscious of the use of plant-based oils in their haircare products which is why many of them started ditching artificial synthetic oils that had damaging effects on scalp health.
That’s when essential oils which are extracted from plants, herbs and flowers started to be widely used in skin and haircare formulation for healthy effects.
These natural oils are derived from natural resources that are high in nutrients like vitamins and fatty acids. A typical ingredient is coconut oil. Almond, argan, babassu, burdock, Castor, and tea seed are among more plant-based sources.
Essential oils used in several hair care products are natural, non-toxic, non-polluting, and biodegradable chemicals with several medicinal properties.
To dive deep into the usage of oils in haircare formulation, let’s understand the types of hair oils.
Types of Hair Oils
There are some common types of oils used in haircare formulation, such as coconut, argan, olive, jojoba, and other essential oils. Let us dive into the unique properties and benefits of each of these oils.
1. Almond Oil
- Its chemical properties or constituents are oleic (62-86%), linoleic (17%), palmitic (5%), myristic (1%), palmitoleic, margaric, stearic, linolenic, arachidic, gadoleic, behenic, and erucic acid glycerides. This oil is easily added in haircare formulation to create shampoos and serums.
- The benefits of almond oil are it has been used for millennia in hair treatment. Almonds have a high vitamin E content. Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant, which means it makes your hair seem younger and healthier. Almond oil is excellent for moisturising hair strands and decreasing breakage and broken ends.
2. Coconut Oil
- Coconut oil is mostly made up of saturated fatty acids (approximately 94%), with many medium-chain fatty acids (over 62%) mixed in. Its antioxidant capabilities are derived from saturated fats such as capric acid, caprylic acid, caproic acid, and myristic acid. Monocaprin and monolaurin are antibacterial and antifungal agents.
- The benefits of coconut oil are that it enhances the shine of hair while smoothing the strands, and is excellent for reducing breakage and split ends. Because of its anti-fungal properties, this oil is useful in maintaining a dandruff-free scalp. It is highly excellent at reducing frizziness and maintaining hydration. During formulation, many formulators choose coconut oil as it is really common to add to hair shampoos, blending oils, and hair masks.
3. Argan Oil
- It contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and E, as well as omega-6 fatty acids, linoleic acid, and antioxidants. Argan oil also includes tocopherols (vitamin E), phenols, carotenes, and squalene in trace amounts. Caffeic acid, oleuropein, vanillic acid, tyrosol, catechol, resorcinol, ()-epicatechin, and (+)-catechin are some trace phenols found in argan oil.
- Argan oil is derived from the seeds of Moroccan Argan fruit plants. Argan oil’s benefit is it is an excellent moisturiser for the hair and scalp. It is also great for adding shine to hair and restoring lacklustre hair. It is incorporated in shampoos and conditioners, providing many benefits while washing the scalp.
4. Olive Oil
- It is mostly composed of oleic acid (up to 83%), with minor levels of other fatty acids such as linoleic acid (up to 21%) and palmitic acid (up to 20%).
- Olive oil, like coconut oil, stimulates your hair’s fibres in a manner that few other oils can. Indeed, the high concentration of monounsaturated fats in olive oil may contribute to its profoundly penetrating, hair-strengthening qualities. As it is so moisturising, olive oil may be able to prevent your hair from winter-related dryness.
- During haircare formulation, olive is commonly chosen by formulators to create hair-blending oils, used in creating hair masks and serums.
Read the benefits of Olivem 1000: A Natural Emulsifier
5. Jojoba Oil
- Gadoleic Acid (Eicosenoic Acid), Erucic Acid, Oleic Acid, Palmitic Acid, Palmitoleic Acid, Stearic Acid, Behenic Acid, Vitamin E, and Vitamin B Complex are the key chemical elements of Jojoba Carrier Oil. Jojoba oil shows antioxidant, anti-acne and anti-prosoriasis, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antipyretic, analgesic, antibacterial, and anti-hyperglycemia effects.
- Jojoba oil, which has long been used in shampoos and conditioners by formulators, may help soften and restore lustre to dull hair. Furthermore, it may help treat dry scalp and reduce dandruff.
Apart from such oils, many essential oils are used in haircare formulation to create different types of shampoos, conditioners, hair oils, serums, hair packs, hair treatment creams and much more. Let’s dive to understand!

Role of essential oils in haircare formulations
To study the incorporation of essential oils in haircare formulation a formulator must know that essential oils are typically complex combinations of volatile secondary metabolites isolated from plants by distillation, expression, or solvent extraction.
They are primarily terpenoid or phenolic in nature, produced by specialised cells from isoprene monomers (C5H8, or (CH2=C(CH3)CH=CH2).
Essential oils are not the same as fixed or fatty oils. Because they have a high vapour pressure at normal temperature, they will totally evaporate if dropped on filter paper, leaving no visible stain.
They can also protect from heat, styling, and colour treatments, and can help to add a glossy shine.
To identify and use essential oils in formulations, specialised equipment such as gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance, or High-Performance Liquid Chromatography is often required by cosmetic formulation scientists.
Alcohols, esters, ethers, ketones, aldehydes, amines, amides, phenols, and heterocyclics are the chemical classifications of essential oils. They are mostly terpenes (approximately 80%), and over 300 low molecular weight volatile chemicals have been found, some of which may have beneficial characteristics.
Some of the most beneficial essential oils are as follows;
- Lavender Oil: Known for its relaxing aroma, lavender oil may help with hair development, hair loss reduction, and scalp health. It may also assist in improving the hair’s general condition and lustre. They are used to create shampoos and hair masks, and while formulating hair oil blends.
- Peppermint Oil: It has a cooling effect and is frequently used to increase hair growth. It may improve blood circulation to the scalp, which may stimulate hair follicle activity. Used in producing scalp-based liquid shots to prevent dandruff and anti-microbial activity, shampoos and conditioners.
- Rosemary oil: It is said to increase scalp circulation, which can aid in hair development and strengthen hair follicles. It’s frequently used to improve hair thickness and general hair health. Used in hair oil blends, shampoos and serums.
- Tea Tree Oil: Because of its antibacterial and antifungal qualities, tea tree oil is excellent for treating scalp disorders such as dandruff and scalp irritation. It can also aid in the maintenance of a clean and healthy scalp. Used while formulating hair oil, hair masks and shampoos.
Oils in common, may that be carrier or essential have a lot of characteristics that play a huge role in haircare formulations which cannot be explained rather by experimenting and formulating and to understand more about the roles and responsibilities of oils in haircare formulation you can opt for our course “certificate of organic haircare formulation” where we teach how to formulate using advanced strategies by incorporating oils in haircare formulation to produce various haircare products thereby assessing the formulas.
Advantages of Incorporating Oils In Haircare Routine
- Preventing Split Ends and Hair Breakage
When you apply oil to your hair, you protect it from breakage caused by brushing and heat styling. Oil also softens your hair, making it less prone to breakage and split ends.
- Hair Growth and Thickness Promotion
Hair oils are high in antioxidants, which stimulate the scalp and encourage growth. Some oils, like coconut oil, include proteins that strengthen your hair while adding volume.
- Scalp Nourishing, Moisturising And Restoring Shine
Oils are high in vitamins and minerals, which nourish and moisturise the scalp. Using oils regularly will help maintain a healthy balance of sebum (natural oil) on your scalp, protecting it from dandruff and other problems.
Hair oils formulated in labs contain botanical blends that nourish hair from root to tip, minimize split ends and frizz, make follicles strong and restore shine.
- Stress Reduction and Relaxation Promotion
For many years, people have utilised essential oils in aromatherapy to decrease tension and promote relaxation. Using oils with relaxing aromas, such as lavender or chamomile, produces a peaceful environment that will aid in the relaxation of your mind and body.
- Getting Rid of Dandruff and Itchy Scalp
Quality hair oils have anti-inflammatory and antifungal characteristics that can alleviate dandruff symptoms such as itching scalp. Oiling your hair will nourish it and relieve itching and flaking on your scalp.
- Oils are naturally UV-protective
Plant phenols contained in herbal oils have the natural capacity to mitigate and even reverse the damaging effects of UV radiation on the skin and hair. Some plant oils give 30% greater protection than bare skin or hair.

Scientific Insights Of Hair-Oil Interaction
To understand the proper mechanism of how oil interacts with hair, we need to analyse the hair structure. Hair has an intriguing structure. It is composed of three separate layers of amino acids (proteins) linked together by chemical bonds.
1. Hair Bulb
The hair bulb, which is located at the base of each hair follicle, houses your growing hair cells. These are constantly dividing and pushing upwards, ultimately strengthening. When they reach the top of the bulb, they separate into six concentric layers.
The follicle is a stocking-like construct that begins in the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. It reaches the dermis, your skin’s second layer.
A patch of tissue called the papilla at the bottom of the follicle comprises microscopic blood vessels (capillaries). These nourish the hair root, allowing it to develop. A hair follicle also houses the germinal matrix, which is where cells grow new hairs.
The cuticle, cortex, and medulla are the three core layers that make up the hair (although the medulla isn’t always present, especially in hairs with a smaller diameter). The outer three layers form the follicular lining.
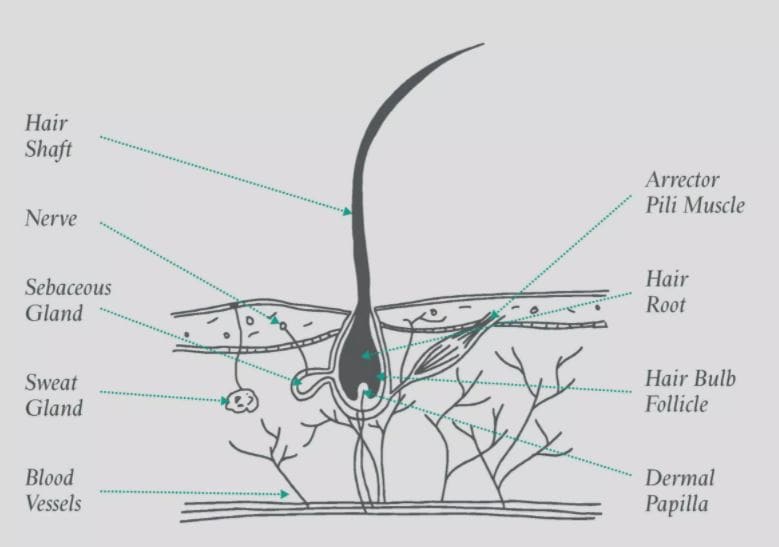
2. Hair Shaft
The visible component of the hair is the hair shaft. The cells are no longer living after the hair grows beyond the skin’s surface. It is composed of three layers of keratin, a protein that hardens. These are the layers:
- The inner layer is known as the medulla. The medulla is not always present depending on the type of hair.
- The cortex, which makes up the majority of the hair shaft, is located in the middle layer. Pigmenting cells, which are accountable for hair colour, are found in the medulla and cortex.
- The cuticle, which is made of tightly packed scales in an overlapping structure resembling roof tiles, forms the outer layer. Many hair conditioners are designed to clean the cuticle by smoothing its framework.
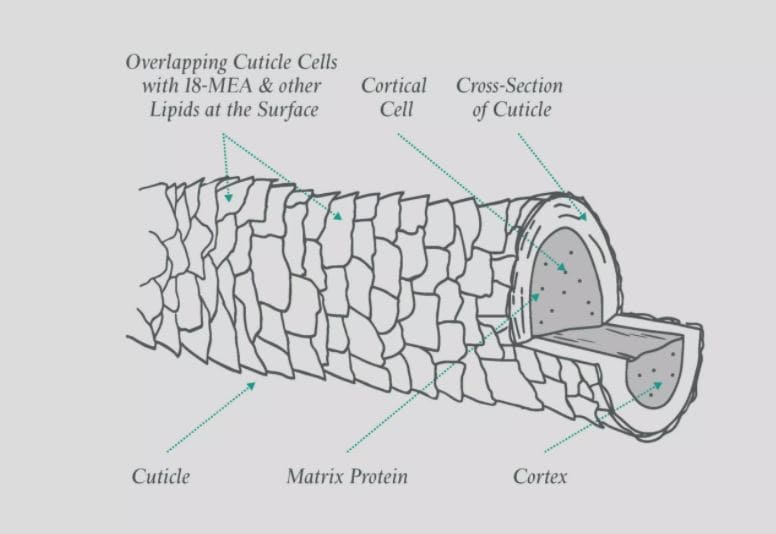
How do oils interact with hair?
It would be challenging to discuss oils in hair penetration without mentioning the chemistry of how it works and why it matter. The triglyceride makeup of an oil is the most essential factor in determining whether it will permeate or seal the hair.
This triglyceride function of oil determines how it will impact hair structure and instil its nutrients on the scalp by combining with amino acids of the keratin protein and structural lipids.
Note: “Triglycerides are esters found in all oils and are composed of glycerol and three fatty acids; that is saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated.”
Different types of oils interact with hair in different ways, not all oils work equally. Scientific studies have mentioned mechanisms of oil interaction with the hair shaft and scalp that modify the internal structure of the hair.
- Penetrating the cortex
Several variables influence the penetration of oil molecule components into hair fibre cross sections. These include the oil’s affinity for the surface of the hair fibre and its capacity to travel the intercellular diffusion channel of the cell membrane complex (CMC).
The molecular mobility of oil is determined by its molecular size, molecular weight (1000 Da), Van der Walls volume, and viscosity.
There have been studies that used ion mass spectrography to observe how oils interact and are absorbed in hair fibre.
For instance, Coconut oil was recognised within the hair fibre cross-section using ion spectra and pictures. Its diffusion ranged from partial to total penetration in depth.
Mineral oil, on the other hand, was not found in the cross-section of hair fibres. The polarity of the two oils was responsible for the discrepancy. Coconut oil, as a triglyceride, is polar in comparison to nonpolar mineral oil. As a result, coconut oil had a stronger affinity for the cortex of hair, which is likewise polar.
So the process of penetration and interaction of oils on the scalp happens like this;
- When oil reaches the surface of the scalp membrane, it gets absorbed by the epidermis, then to the dermis and then to adipose tissue.
- In the epidermis, oils first get absorbed into the hair papilla from which the components of the oil get distributed by the blood vessels connected to the papilla.
- Then it spreads to the hair bulb, hair root, and hair erector muscle. Through that muscle, it then gets transferred to the hair shaft, thereby affecting the structure of the cortex, cuticle and medulla.
- After it enters the cuticle it gets into the cortex, where it interacts with macro and microfibril, intermediate filament, tetramer, keratin protein and amino acids within those proteins.
- These oil enzymes and chemicals then interact with amino acids of keratin protein thereby providing necessary nutrients and vitamins to the structures’ amino acids, which leads to affecting the hair structure, their components, hair growth, thickness, shine, moisture, elasticity and tensile strength.
- As cuticle protects the layers within, they regulate how much oil’s moisture penetrates inner layers, thereby controlling moisture retention on hair follicles and shaft.
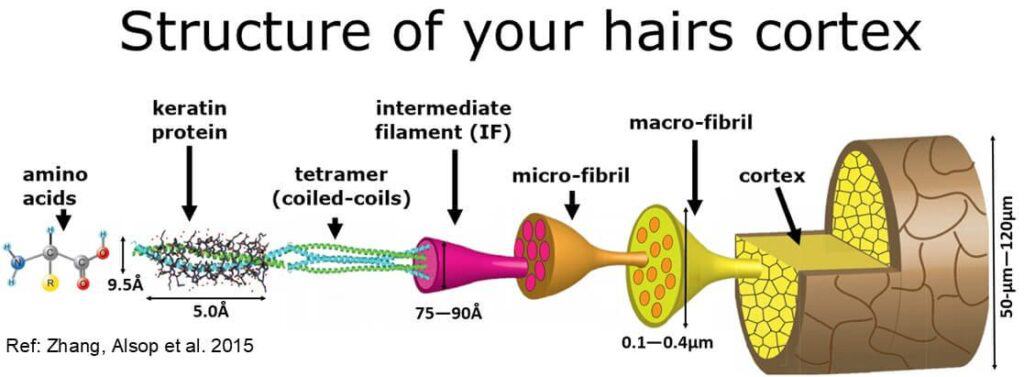
Fig 3.: Hair structure shows how oil impacts hair layers & cortex (IMG from hairknowhow)
- Strengthening and Moisturizing The Hair Shaft
Some fatty-rich oils have compounds that penetrate the hair shaft, giving parched hair much-needed moisture. They can also form a protective layer on the hair shaft and cortex, which aids in moisture retention.
Study shows that molecules that makeup oil must be tiny enough to permeate the hair bulb follicle, hair shaft’s cuticle, cortex and hair roots to replace moisture and improve hair health.
Hair oils that are formulated in labs are sometimes made from hydrolyzed proteins, which are often derived from a plant source like wheat. Hydrolysis is the process of breaking down proteins so that they can dissolve in water.
These proteins bind to the hair, promoting temporary repair of broken regions. As a result, hair becomes stronger and appears healthier.
Our Formulation Of Hair Oil Blends
Blend 1: Oil for Hair Growth
Ingredients Needed:
- Rosehip seed oil: 65%
- Castor oil: 15%
- Jojoba oil: 18%
- Vitamin E: 0.8%
- Rosemary essential oil: 1%
- Lavender essential oil: 0.2%
Directions:
- In a glass or any biodegradable container that has a lid on it, combine all these ingredients mentioned according to the measurement put the lid on, and give it a few good shakes to let it blend properly.
- Transfer to a storage container or emptied pump bottle to use.
- This DIY oil for hair growth works best when applied to damp hair. Depending on your hair type, apply once or twice a week up to once a day.
Note: Oil for hair growth, is high in vital fatty acids, antioxidants, and nutrients, and work together to address concerns such as hair loss, brittleness, and dullness while also providing deep hydration and conditioning. Certain oils such as castor oil, coconut oil, black seed oil, Bhringraj, Argan and Indian gooseberry, deliver important nutrients straight to the scalp, which is critical for fostering healthy hair growth.
Blend 2: All-purpose hair oil:
Ingredients Needed:
- Castor Oil: 20%
- Coconut Oil: 15%
- Rosemary Essential Oil: 1%
- Argan Oil: 18%
- Jojoba Oil: 15%
- Almond Oil: 10%
- Olive Oil: 10%
- Grapeseed Oil: 10%
- Vitamin E- 0.8%
- Lavender Essential Oil: 0.2%
Directions:
- In a glass or any biodegradable container that has a lid on it, combine all these ingredients mentioned according to the measurement. Put the lid on, and give it a few good shakes to let it blend properly.
- Transfer to a storage container or emptied pump bottle to use.
- This DIY all-purpose hair oil works best when applied to damp hair. Depending on your hair type, apply once or twice a week up to once a day.
You may alter the ratios based on your tastes and hair type. These blends contain a variety of oils known for their specific benefits, such as hair development, nourishment, and general hair health. Before using essential oils on your hair and scalp, always conduct a patch test to confirm you are not allergic to them.

Methods Of Hair Oiling
- Apply oil to dry hair and keep it on for a few hours or a day or sometimes you can keep it overnight. To thoroughly clean it, use shampoo.
- After showering or bathing, apply oil to damp hair. This will help to seal in moisture and lustre to your hair.
- When styling your hair, use it as a leave-in conditioner. It will control frizz, add shine, and give long-lasting conditioning.
- Used to protect frizzy or damaged hair from heat styling.
- Before going to bed, apply to towel-dried hair. This will assist your hair in retaining moisture and appearing smoother in the morning.
Concluding The Scene
From the above paragraphs, we conclude that in-depth research is required to understand the chemical and medicinal properties of various plant-based oils (as we don’t encourage using synthetic ones) to grasp how the oil components work in formulations and how oils can be used in a measurable way in haircare formulations to create haircare products such as shampoos, hair oil blends, conditioners, serums, hair masks, hair styling products and much more.
Formulating hair oil isn’t easy and can be daunting for formulators, due to the lack of understanding of proportional measurements, efficacy, blending methods and other factors. But we at Learn Canyon teach formulators about some of the most cutting-edge chemicals in the global beauty business and how to produce high-performance, organic haircare formulations using plant-based oils.
Begin by creating at least one successful haircare product, and who knows, you could be the next success story in the long line of Learn Canyon Diploma Graduates.











2 thoughts on “Oils in Haircare Formulations: Roles & Responsibilities”
Thanks so much for this active it very useful .
Thanks so much for this article, is very useful.